Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=TOCOL(array,ignore,scan_by_column)- array - The array to transform.
- ignore - Setting to ignore blanks and errors.
- scan_by_column - Scan array by column. TRUE = by column, FALSE = by row (default).
Using the TOCOL function
The TOCOL function transforms an array or range into a single column. By default, TOCOL will scan values by row, left to right. However, TOCOL can also be configured to scan the array by column, top to bottom. TOCOL also provides options for skipping empty cells and errors.
The TOCOL function takes three arguments: array, ignore, and scan_by_column. Array is the only required argument and represents the array or range to be transformed. The ignore argument controls what values TOCOL will optionally ignore. The options for ignore are as follows:
| Value | Purpose |
|---|---|
| 0 (default) | Keep all values |
| 1 | Ignore blanks |
| 2 | Ignore errors |
| 3 | Ignore blanks and errors |
The scan_by_column argument is a boolean value that controls how TOCOL reads values from the source array. By default, scan_by_column is FALSE and TOCOL will read values "by row" from left to right. At the end of each row, TOCOL will drop down and read values from the next row in the same order. To read values instead by column, set scan_by_column to TRUE or 1. In this mode, TOCOL will read values from top to bottom in the first column in the array, then move one column to the right, and read the next column in the same order.
Use the TOCOL function to transform an array into a single column and the TOROW function to transform an array into a single row. The TRANSPOSE function will transpose an array from horizontal to vertical and vice versa, but it won't restructure the array.
Basic usage
By default, the TOCOL function transforms a two-dimensional array into a single column, working through the array one row at a time. In the example below, the formula in F4 is:
=TOCOL(B4:D5)

TOCOL converts the 2 x 3 array in B4:D5 into the 6 x 1 array in F4:K9.
Note: In Excel, arrays map directly to ranges. Technically, the array is converted and the result lands in cell F4, where it spills into the range F4:F9.
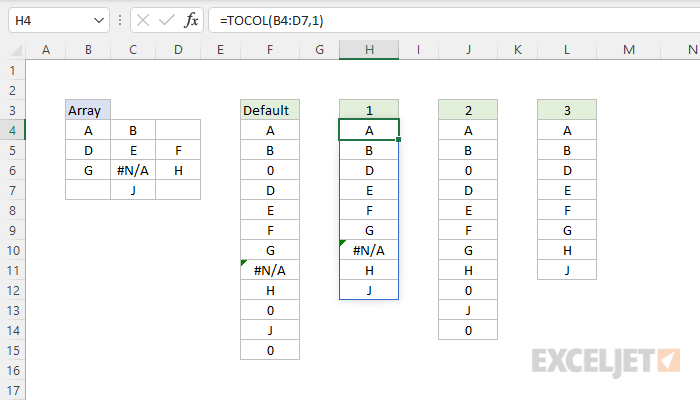
Ignore blanks and errors
The ignore argument in TOCOL can be set to ignore blanks and/or errors like this:
=TOCOL(array) // default
=TOCOL(array,1) // ignore blanks
=TOCOL(array,2) // ignore errors
=TOCOL(array,3) // ignore blanks and errors
The screen below shows how these options work with the range B4:D7, which contains both blanks and errors.
Scan by column
By default, TOCOL will read values "by row" from left to right. To read values instead by column, set scan_by_column to TRUE or 1. The worksheet below shows the default "by row" behavior in F4. In cell H4, scan_by_column is set to TRUE:
=TOCOL(B4:D5,,TRUE)

Notice the resulting array is the same size, but the values appear in a different order. Also note the optional ignore argument has been left empty.