Pivot tables are an easy way to quickly average unique values in a data set, and can easily be adapted to perform a two-way average. In the example shown above, a pivot table is used to average Ratings for unique combinations of Age and Gender, based on data in the range B5:D16, defined as an Excel Table.
Fields
The pivot table shown is based on three fields: Age, Gender, and Rating. The Age field is added as a Row field, and the Gender field is added as a Column field. The Rating field is added as a Value field:
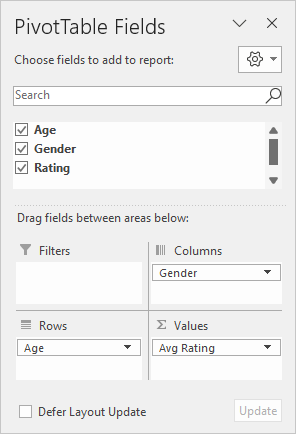
The Rating field in the Values area is renamed to "Avg Rating" and configured to Average:
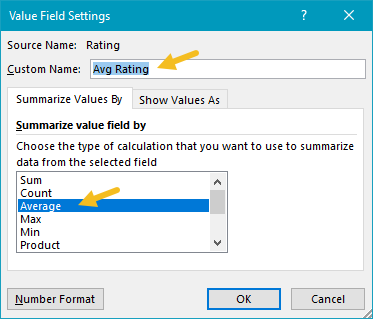
The custom name can be anything except an existing source field name (i.e. not "Age", "Gender", or "Rating").
Steps
- Define data as an Excel Table (optional)
- Create a pivot table based on a table or data
- Add the Age field to the Rows area
- Add the Gender field to the Columns area
- Add the Rating field to the Values area
- Change Rating calculation to Average
- Rename Rating field (optional)
Notes
- When a numeric field is added as a Value field, Excel the field is automatically summed.
