Explanation
In this example, the goal is to write a formula that will return TRUE if a year is a leap year and FALSE if not. This is a surprisingly challenging problem in Excel for two reasons: (1) Excel thinks 1900 is a leap year due to a long-standing bug inherited from Lotus 1-2-3 and (2) The logic for testing a leap year is not intuitive and requires some understanding of the history of the Gregorian calendar system we use today. Both topics are discussed in more detail below.
Quick and dirty solution
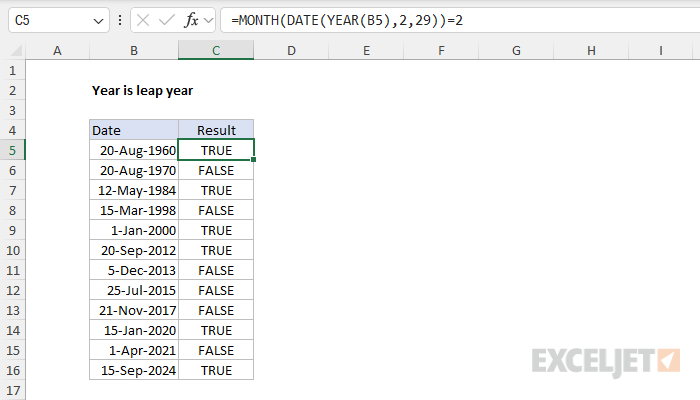
In the worksheet shown above, we use a quick and dirty formula to check for leap years. The core of this formula is the DATE function, which will automatically adjust to month and year values that are out of range. In the formula, the year is extracted with the YEAR function. Then it is passed into the DATE function, along with 2 for the month (February) and 29 for the day:
DATE(YEAR(B5),2,29)
Then we wrap the MONTH function around that formula and check if the month is 3:
=MONTH(DATE(YEAR(B5),2,29))=2 // returns TRUE or FALSE
What's going on here? The answer depends on a subtle behavior in Excel's date system. In a leap year, February has 29 days, so the DATE function will simply return the date February 29 in the given year. For example, when the year is 1960, DATE returns the valid date 29-Feb-1960:
DATE(1960,2,29) // returns "29-Feb-1960"
However, in a non-leap year, DATE will return March 1 in the given year, because there is no 29th day in February. In other words, the DATE function rolls the date forward to the next valid date. For example, if we change the year to 1961, we get the date 1-Mar-1961:
DATE(1961,2,29) // returns "1-Mar-1961"
The MONTH function then extracts the month from the date and checks if the month number is 2. If the result is TRUE, we have a leap year. If the result is FALSE (the month is 3), the year is not a leap year.
Testing the year only
In the worksheet shown, we are extracting the year from a date with the YEAR function before testing for a leap year. To test a year value only, just remove the YEAR function from the formula:
=MONTH(DATE(year,2,29))=2
In this version, we don't extract a year value from a date, we pass a year value (i.e. 1960) directly to the DATE function.
Limitations
Although the formulas above are clever and efficient, they have two limitations you should be aware of:
- They incorrectly report 1900 as a leap year (see below for details).
- They only work with dates/years after January 1, 1900.
These limitations arise because the formulas are built directly on Excel's date system. The first limitation is easy to work around, as explained in the next section. The second limitation is more fundamental and requires a different approach.
Excel's 1900 problem
Excel erroneously treats 1900 as a leap year. This is due to a legacy bug from compatibility with Lotus 1-2-3, an older spreadsheet application that also erroneously treated 1900 as a leap year. Unfortunately, this means the formulas above will incorrectly return TRUE if you are testing for a leap year with dates in 1900. You can guard against this problem with a simple hack like this:
=AND(MONTH(DATE(YEAR(B5),2,29))=2,YEAR(B5)<>1900)
This version of the formula enforces two conditions with the AND function:
- The month of the adjusted date must be 2.
- The year must not be equal to 1900.
Both conditions must be TRUE or else the formula will return FALSE. This is a simple way to avoid classifying 1900 as a leap year. However, to test year values earlier than 1900, we need a new approach, because Excel's date functions will only work with dates beginning with January 1, 1900. However, before we look at a solution, I need to introduce the Julian and Gregorian calendars.
The Julian and Gregorian calendars
The formulas below don't make sense unless you know a little about the history of the Julian and Gregorian Calendars. The Julian Calendar was a system of dates instituted by Julius Caesar in 46 BC. This calendar added one extra day every four years, based on the calculation that it takes 365.25 days for the earth to travel around the sun, not exactly 365 days. The idea was to account for an extra day every four years, creating a "leap year". However, it turns out this calculation is not correct. The sun's trip around the sun is not exactly 365.25 days but 365.24237 days, approximately 11 minutes less. As a result, the Julian Calendar was over-correcting by about 8 days every 1000 years.
Further study in the 16th century resulted in a better solution. The idea was that centenary years would not be leap years unless they were divisible by 400. This meant three out of four centenary years would not be leap years. In other words, every 400 years there would be 97 leap years instead of 100 leap years. In 1582, Pope Gregory ruled that the new date system (called the "Gregorian Calendar" thereafter) should replace the Julian Calendar. In simple language, the rule for leap years is as follows:
To be a leap year, the year number must be divisible by four – except for end-of-century years, which must be divisible by 400. This means that 2000 is a leap year, but 1700, 1800, and 1900 are not leap years.
The long-form formula below is meant to follow this logic.
Classic leap year formula
Now that we understand the basic history of leap years in our calendar system, we can look at how to implement a leap year rule in Excel. To handle years before 1900, we need a math-based formula that doesn't require Excel's date functions. The classic long-form formula to test for a leap year looks like this:
=IF(MOD(A1,400)=0,TRUE,IF(MOD(A1,100)=0,FALSE,IF(MOD(A1,4)=0,TRUE,FALSE)))
Here, A1 contains a year value like 1985, 2005, etc. This formula uses the MOD function to test if the year is evenly divisible by 400, 100, and 4 and applies this logic to determine if the year is a leap year:
- If the year is divisible by 400, it's a leap year (TRUE).
- If the year is not divisible by 400 but is divisible by 100, it is not a leap year (FALSE)
- If the year is not divisible by 100 but is divisible by 4, it's a leap year (TRUE).
The same logic can be condensed by replacing the nested IF construction above with the AND and OR functions like this:
=OR(MOD(A1,400)=0,AND(MOD(A1,4)=0,MOD(A1,100)<>0))
- If the year is divisible by 400, it's a leap year (TRUE).
- Or if the year is divisible by 4 and not divisible by 100, it's a leap year (TRUE)
- Otherwise, the year is not a leap year (FALSE).
Both formulas above work well, and both correctly report 1900 as a non-leap year. The formulas are a bit longer and less intuitive, but both formulas can be used to test year values before 1900. By contrast, the original "short" formulas at the top of this page depend on Excel's date engine and won't handle dates or years before 1900.