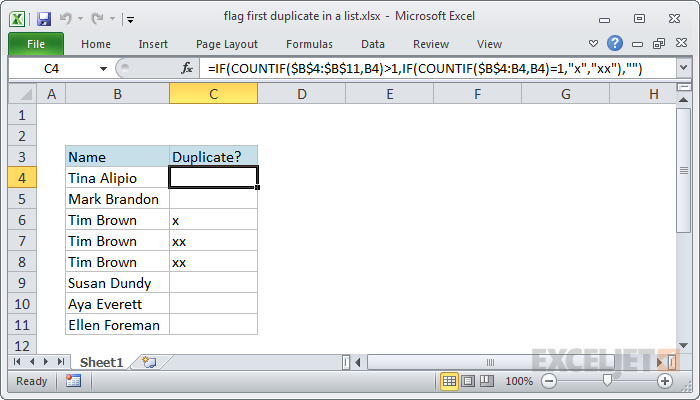
Explanation
At the core, this formula is composed of two sets of the COUNTIF function wrapped in the IF function. The outer IF + COUNTIF first checks to see if the value in question (B4) appears more than once in the list:
=IF(COUNTIF($B$4:$B$11,B4)>1
If not, the outer IF function returns an empty string ("") as a final result. If the value does appear more than once, we run another IF + COUNTIF combo. This one does the work of flagging duplicates:
IF(COUNTIF($B$4:B4,B4)=1,"x","xx")
This part of the formula uses an expanding reference ($B$4:B4) that expands as the formula is copied down the column. The first B4 in the range is absolute (locked), and the second is relative, so it changes as the formula is copied down the list.
Remember that this part of the formula is only executed if the first COUNTIF returns a number greater than 1. So, at each row, the formula checks the count inside the range up to the current row. If the count is 1, we mark the duplicate with "x", since it's the first one we've seen. If it's not 1, we know it must be a subsequent duplicate, and we mark it with "xx"
Basic formula
To flag the first duplicate in a list only with a 0 or 1, you can use this stripped-down formula, which uses an expanding range and the COUNTIFS function.
=(COUNTIFS($B$5:B5,B5)=2)+0
This formula will return 1 only when a value has been encountered twice – the first occurrence will return zero:
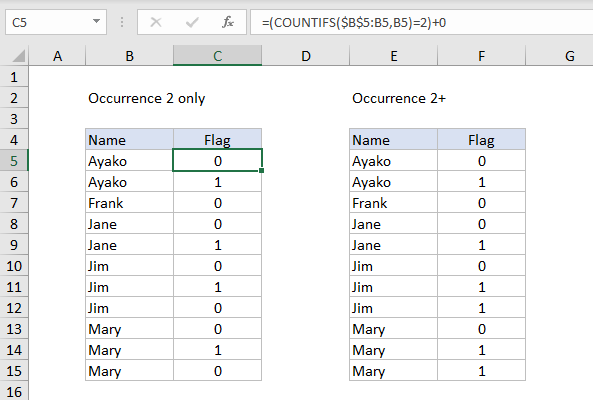
To flag the second and all subsequent occurrences, the formula in F5 above is:
=(COUNTIFS($E$5:E5,E5)>=2)+0
Note: In both examples, adding zero is just a simple way to coerce TRUE and FALSE values to 1 and 0.
Also, using COUNTIFS instead of COUNTIF makes it possible to evaluate values in other columns as part of the test for duplicates. Each additional column also needs to be entered as an expanding range.