Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=GAMMALN.PRECISE(x)- x - A positive real number for which you want to calculate the natural logarithm of the gamma function.
Using the GAMMALN.PRECISE function
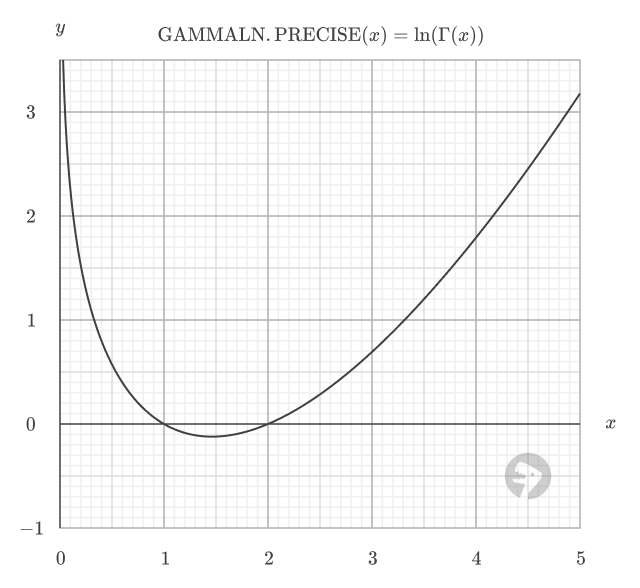
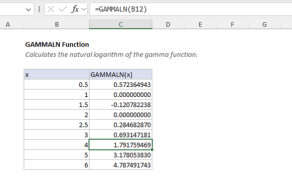
The GAMMALN.PRECISE function returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, ln(Γ(n)), for a given number. This is useful in statistical calculations, such as those involving probability distributions, where the gamma function appears in the denominator and direct computation could result in very large or very small numbers.
For positive integers n, GAMMALN.PRECISE(n) is equivalent to LN((n-1)!). For example, the following formula calculates the natural logarithm of the gamma value for 5:
=GAMMALN.PRECISE(5) // returns 3.17805383
Key features
- Returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function for decimal numbers
- For positive integers n, GAMMALN.PRECISE(n) equals LN((n-1)!)
- Accepts positive decimal numbers as input
- Returns #NUM! error for zero and negative numbers
- More accurate than the legacy GAMMALN function
Table of contents
- Key features
- Example #1 - Basic calculations
- Example #2 - Relationship to gamma and factorials
- Example #3 - Error conditions
- Formula definition
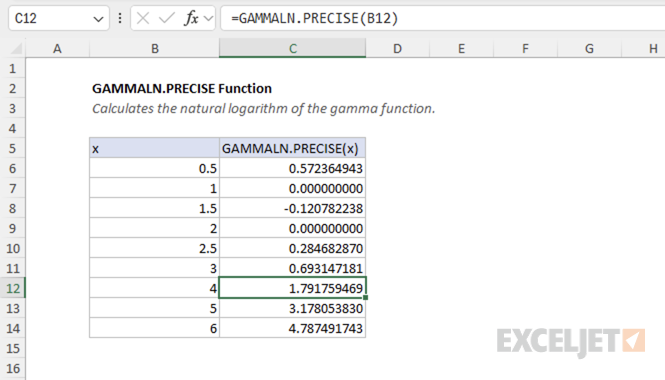
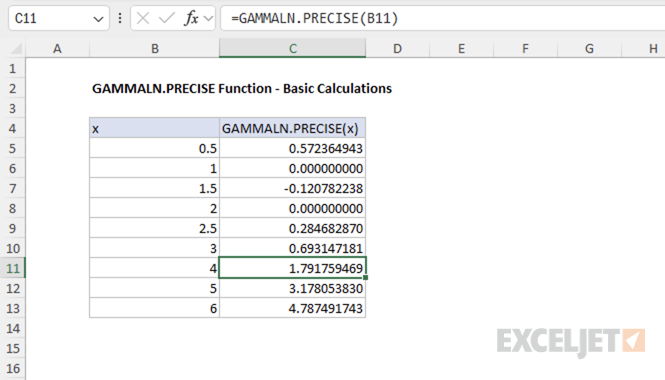
Example #1 - Basic calculations
The GAMMALN.PRECISE function takes a single argument as input like this:
=GAMMALN.PRECISE(x)
The argument x is the value for which you want to calculate the natural logarithm of the gamma function. Here are some basic examples showing both integer and non-integer inputs:
=GAMMALN.PRECISE(0.5) // returns 0.57236494...
=GAMMALN.PRECISE(2.0) // returns 0
=GAMMALN.PRECISE(2.5) // returns 0.28468287...
=GAMMALN.PRECISE(4.0) // returns 1.79175947...
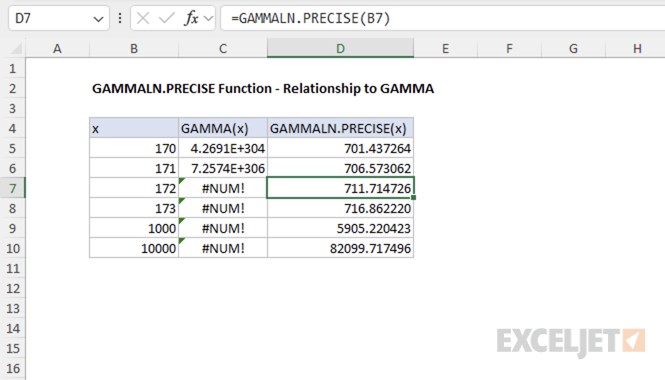
Example #2 - Relationship to gamma and factorials
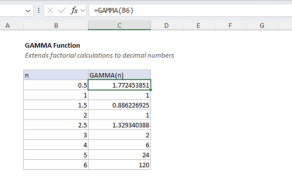
In general, the GAMMALN.PRECISE function is equivalent to the natural logarithm of the gamma function:
=GAMMALN.PRECISE(x) // returns LN(GAMMA(x))
This relationship makes the GAMMALN.PRECISE function useful for calculations involving large factorials, as it avoids direct computation of large numbers. For example, attempting to compute a large factorial directly with the GAMMA function can result in an error due to overflow:
=GAMMA(172) // returns #NUM! error
In contrast, using GAMMALN.PRECISE allows you to work with the logarithm of the gamma function, which avoids this problem and provides a valid result even for large inputs.
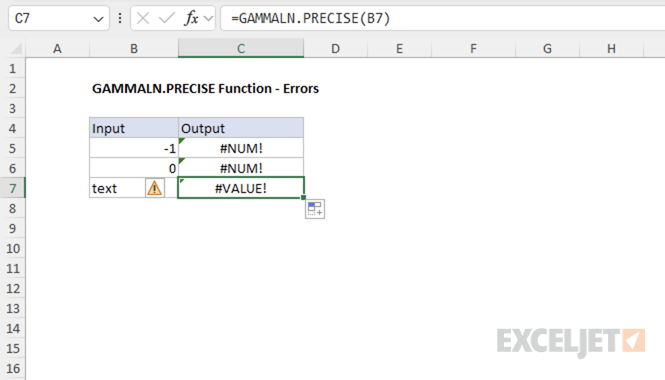
Example #3 - Error conditions
The GAMMALN.PRECISE function returns #NUM! for zero and negative numbers, and #VALUE! for non-numeric inputs.
=GAMMALN.PRECISE(0) // returns #NUM! error
=GAMMALN.PRECISE(-1) // returns #NUM! error
=GAMMALN.PRECISE(-2.5) // returns #NUM! error
=GAMMALN.PRECISE("text") // returns #VALUE! error
Formula definition
The GAMMALN.PRECISE function is defined as the natural logarithm of the gamma function. The function is mathematically equivalent to:
GAMMALN.PRECISE(x) = LN(GAMMA(x))
The function is plotted below, where Γ(x) is the gamma function.