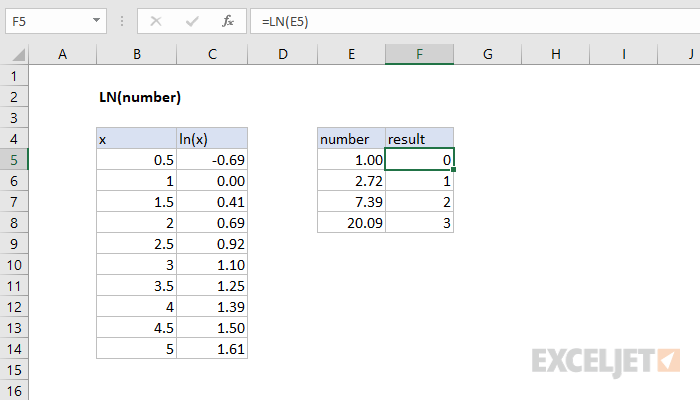
Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=LN(number)- number - A number to take the natural logarithm of.
Using the LN function
The LN function returns the natural logarithm of a given number. The natural logarithm is equivalent to log base e of a number, where e is Euler's number, a mathematical constant with the approximate value 2.71828182845904. The LN function is the inverse of the EXP function and is used to model exponential decay.
The LN function takes just one argument, number, which should be a positive number.
Examples
=LN(1) // returns 0
=LN(e) // returns 1
=LN(e^2) // returns 2
The equivalent form of the natural logarithm function is given by:
=LN(number)=LOG(number,e) // Where e ≈ 2.7128 or EXP(1)
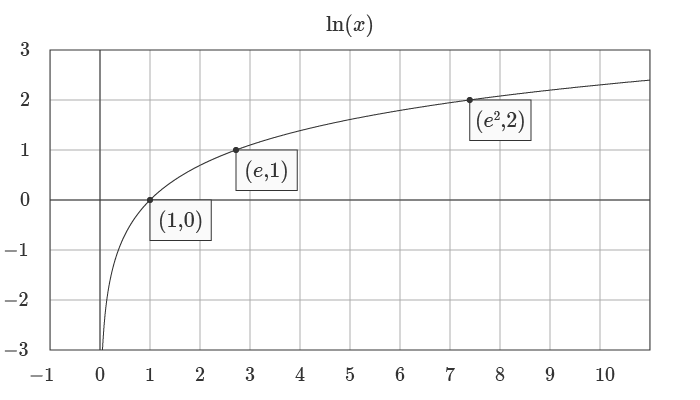
Graphs
Below is a graph of the natural log logarithm:
The natural logarithm function and exponential function are the inverse of each other, as you can see in the graph below:
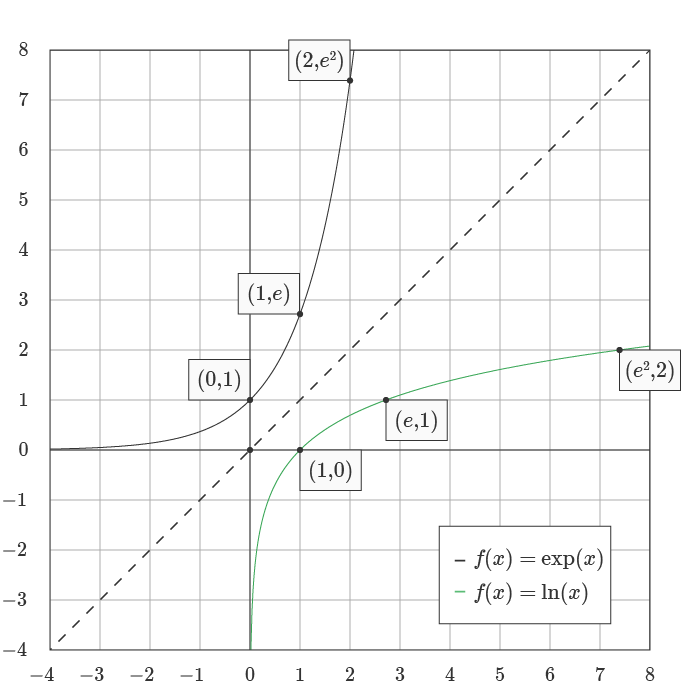
This inverse relationship can be represented with the formulas below, where the input to the LN function is the output of the EXP function:
= LN(EXP(1)) // returns 1
= LN(EXP(2)) // returns 2
= LN(EXP(n)) // returns n
See wumbo.net for a more detailed explanation of key math concepts and formulas.
Notes
- The natural logarithm function can be defined as the area under a hyperbola.
- The function is used in applications relating to compound interest.