Explanation
In this example, the goal is to add hours in decimal format (i.e. 1, 2, 3, etc.) to an existing Excel time. The complication is that Excel stores time as fractional values. The number 0.25 makes sense when you consider that 6 hours is one-quarter of a day, and a day in Excel equals 1. But it isn't the way most people think about time. To add decimal hours to a time, we need to first convert the hours to an equivalent fractional value.
How Excel tracks time
In Excel, dates are serial numbers, so a single day has a numeric value of 1. As a result, time is a fractional value of 1 and 1 hour = 1/24 = 0.041666667. This means that 6 hours is one-quarter of a day (0.25), 12 hours is half a day (0.5), 18 hours is three-quarters of a day (0.75), and 24 hours is 1 day. In the same way, 6:00 AM has a numeric value of 0.25, 12:00 PM has a value of 0.5, and 6:00 PM has a value of 0.75. The table below summarizes this relationship:
| Hours | Time | Fraction | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 12:00 AM | 0/24 | 0 |
| 3 | 3:00 AM | 3/24 | 0.125 |
| 6 | 6:00 AM | 6/24 | 0.25 |
| 4 | 4:00 AM | 4/24 | 0.167 |
| 8 | 8:00 AM | 8/24 | 0.333 |
| 12 | 12:00 PM | 12/24 | 0.5 |
| 18 | 6:00 PM | 18/24 | 0.75 |
| 21 | 9:00 PM | 21/24 | 0.875 |
| 24 | 12:00 AM | 24/24 | 1.0* |
* In Excel, midnight (12:00 AM) has a dual nature: it has a value of 0 when it represents the start of a day, but it can be 1 inside a calculation that completes a full 24-hour cycle. In other words, as we approach midnight, the value of time approaches 1. But as we cross from one day to another, the 1 is added to the date, and time begins again at zero.
Adding decimal hours to a time
Because Excel stores time as fractional values, we need to convert decimal hours to a valid time before addition. To do this, we simply divide the hours by 24. For example, with an Excel time in cell A1, we can add 3, 6, 12, and 18 hours like this:
=A1+(3/24) // add 3 hours
=A1+(6/24) // add 6 hours
=A1+(12/24) // add 12 hours
=A1+(18/24) // add 18 hours
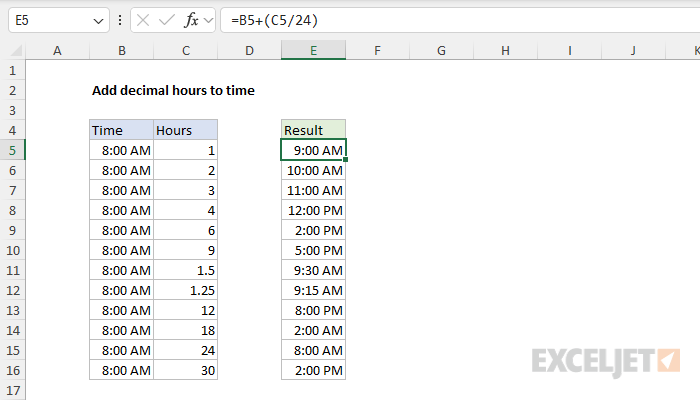
In the example shown, the formula in cell E5 uses the same idea above like this:
=B5+(C5/24)
As the formula is copied down, it adds the decimal hours in column C to the times in column B. The results in column E are formatted with the custom number format "h:mm AM/PM".
With the TIME function
You can also add time values with the TIME function. To add 15 hours to a time in A1, use:
=A1+TIME(6,0,0)
The TIME function saves you from having to remember the formula for converting decimal hours to an Excel time. However, note that the TIME function only supports time spans up to 24 hours. Every 24 hours, the time will reset to zero like a clock. For example, the formulas below show what happens if we use 25 hours:
=TIME(25,0,0) = 0.041667 = 1:00 AM same day (1 hr)
=25/24 = 1.041667 = 1:00 AM next day (25 hrs)
The TIME function returns the equivalent of 1 hour, while =25/24 returns the full value.
Subtracting hours from time
You may get an error if you try to subtract hours from a time when the result is negative because Excel doesn't support negative time values. One way to avoid this problem is to use a formula like this:
=MOD(time-(hours/24),1)
Here, the MOD function takes care of the negative problem by using the MOD function to "flip" negative values to the required positive value. Another way to avoid this problem is to start with a time that includes a date. This lets you subtract very large numbers of hours without any danger of getting a negative result. If you don't want to see the date displayed in the result, just apply a time-only number format. For a more detailed discussion of this topic see Calculate hours between two times.
Working with dates + times
A good way to simplify formulas and avoid negative time values is to use a date that includes a time value, sometimes called a "datetime", as the starting value. This lets you subtract a large number of hours without the danger of getting a negative result. You can see how this works in the worksheet below, where the values in column B contain a date and a time. The formula in cell E5 is the same as the original above:
=B5+(C5/24)
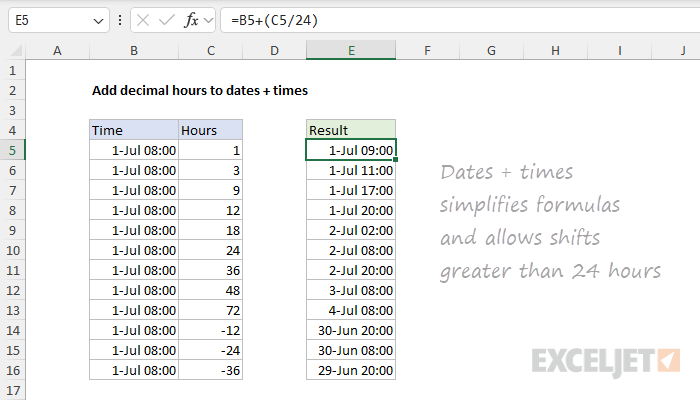
Because values in column B contain a date, the numbers are very large. For example, the numeric value in cell B5 is 45474.3333. As a result, we are able to add or subtract a large number of hours with one simple formula. Notice the results in rows 14-16 are valid and work fine. All values in columns B and E are formatted with the same custom number format:
d-mmm hh:mm
You can customize this format in any way you like.