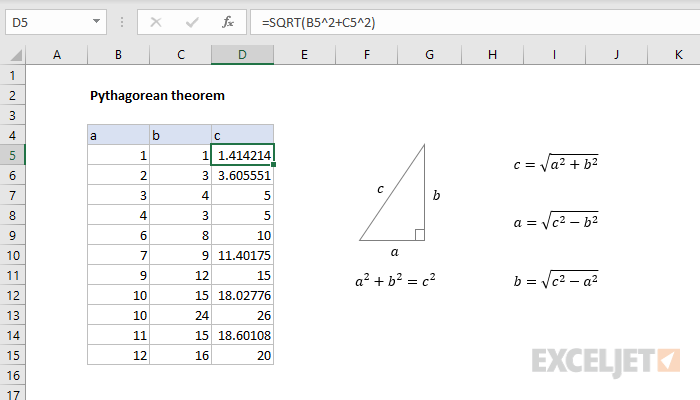
Explanation
The Pythagorean theorem is a key principle in Euclidean geometry. It states that the square of the longest side of a right triangle (the hypotenuse) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. The theorem is written as an equation like this:
a2 + b2 = c2
When any two sides are know, this equation can be used to solve for the third side. When a and b are known, the length of the hypotenuse can be calculated with:
When b and c are known, the length of side a can be calculated with:
When a and c are known, length of side b can be calculated with:
To translate the above into Excel formula syntax, use the exponentiation operator (^) and the SQRT function, as seen below. The Pythagorean theorem can be written as:
=a^2+b^2=c^2 // Pythagorean theorem
And the formulas below can be used to solve for each of the three sides:
c=SQRT(a^2+b^2) // hypotenuse
a=SQRT(c^2-b^2) // side a
b=SQRT(c^2-a^2) // side b
Instead of the exponentiation operator, you can also use the POWER function like this:
c=SQRT(POWER(a,2)+POWER(b,2))
a=SQRT(POWER(c,2)-POWER(b,2))
b=SQRT(POWER(c,2)-POWER(a,2))
The formulas above are an example of nesting one function inside another.