Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=EXP(number)- number - The power that e is raised to.
Using the EXP function
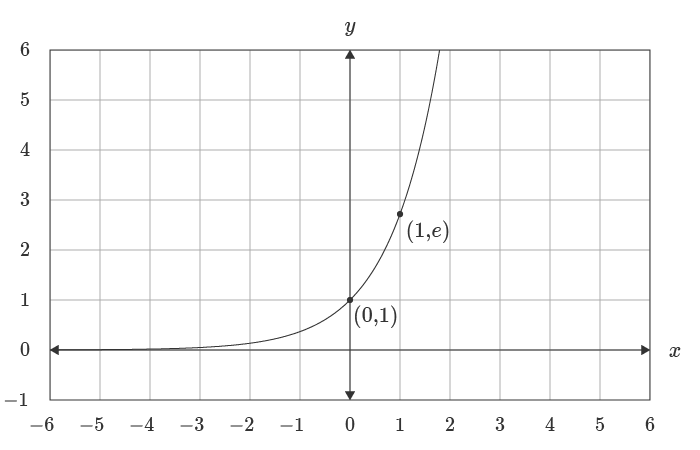
The EXP function finds the value of the constant e raised to a given number, so you can think of the EXP function as e^(number), where e ≈ 2.718. The exponential function can be used to get the value of e by passing the number 1 as the argument.
=EXP(0) // returns 1
=EXP(1) // returns 2.71828182846 (the value of e)
=EXP(2) // returns 7.38905609893
The exponential function models exponential growth and has the unique property where the output of the function at a given point is proportional to the rate of change of the function at that point. The inverse of the exponential function is the natural logarithm which represents the opposite of exponential growth, exponential decay.
For a more detailed explanation see wumbo.net.
Notes
- e stands for Euler's number.
- The number e is a famous irrational number, and one of the most important numbers in mathematics.
- The first digits of e are: 2.718281828459...
- e is the base of the Natural Logarithms, invented by John Napier.









