Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=COT(number)- number - The angle provided in radians.
Using the COT function
The Excel COT function returns the cotangent of an angle provided in radians. In geometric terms, the cotangent of an angle returns the ratio of the length of the adjacent side over the length of the opposite side of the corresponding right triangle. For example, the cotangent of PI()/6 (30°) returns the ratio 1.732.
=COT(PI()/6) // Returns 1.732
Using Degrees
To supply an angle to COT in degrees, multiply the angle by PI()/180 or use the RADIANS function to convert to radians. For example, to get the COT of 60 degrees, you can use either formula below:
=COT(60*PI()/180)
=COT(RADIANS(60))
Explanation
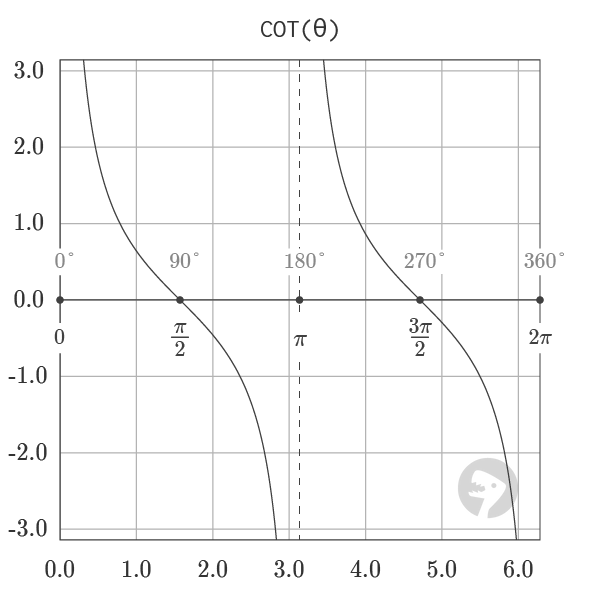
The graph of COT, shown above, visualizes the output of the function for angles from 0 to a full rotation. The function has vertical asymptotes at the points 0, π, and 2π where the output of the function diverges to infinity. The COT function is the reciprocal of TAN and can be equivalently defined in the formula below:
=COT(angle)=1/TAN(angle)
The reciprocal relationship between COT and TAN is visualized by the graph shown below of both of the functions plotted together.
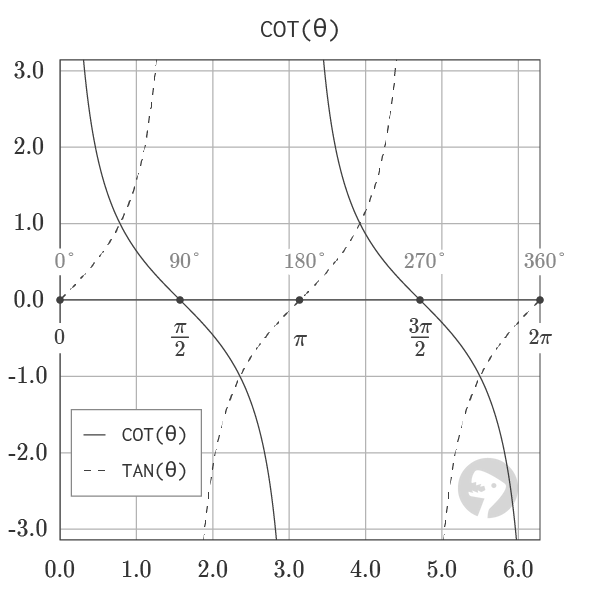
Graphs courtesy of wumbo.net.










