Explanation
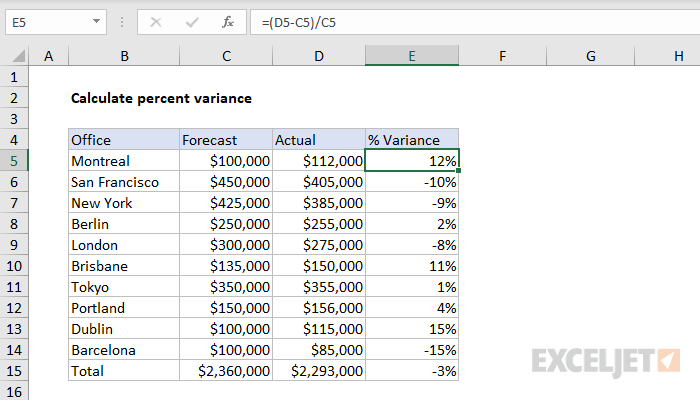
In this example, the goal is to calculate the variance between a Forecast (column C) and Actual (column D) as a percentage. For example, with a Forecast value of 100,000 and an Actual value of 112,000, we want to return a variance of 12%.
The concept of variance requires a baseline value and a "new" value. The baseline value is subtracted from the new value and the result is divided by the baseline value. The general formula, where "x" is the variance, is:
x=(new-baseline)/baseline
x=(112,000-100,000)/100,000
x=12,000/100,000
x=0.12
After converting to an Excel formula with cell references, the formula in E5, copied down, is:
=(D5-C5)/C5
=(112,000-100,000)/100,000
=12,000/100,000
=0.12
=12%
As the formula is copied down, it returns a decimal number for each item in the list. When these numbers are formatted with the Percentage number format, they are displayed as percentages.
Formatting percentages in Excel
In mathematics, a percentage is a number expressed as a fraction of 100. For example, 25% is read as "Twenty-five percent" and is equivalent to 25/100 or 0.25. Accordingly, the values in column E are decimal values, with the Percentage number format applied. To convert these values to a whole number like 12, multiply by 100:
=(D5-C5)/C5*100
Negative numbers
If you have a negative value for the original number, the above formula won't work and can be adjusted by adding the ABS function:
=(new-original)/ABS(original)
ABS stands for "absolute value", and it converts negative values to positive values. In this case, the ABS function ensures the original value is positive when the variance is calculated.
Note: be aware that results negative values can be misleading, as explained by Jon Acampora in his detailed article on the topic.