Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=ROMAN(number,[form])- number - Number (in Arabic numeral) you want to convert to Roman numeral.
- form - [optional] The type of Roman numeral you want.
Using the ROMAN function
The ROMAN function converts a number to a Roman numeral. For example:
=ROMAN(4) // returns "IV"
=ROMAN(9) // returns "IX"
=ROMAN(99) // returns "XCIX"
=ROMAN(100) // returns "C"
ROMAN takes two arguments: number and form. Number should be a whole number between 1 and 3999. The form argument controls the convention used for Roman numbers. The argument is optional and the default is zero (0), which results in classic non-abbreviated Roman numbers. Other possible values are 1-4, which specify progressively more concise output. For example:
=ROMAN(1999,0) // returns "MCMXCIX"
=ROMAN(1999,2) // returns "MXMIX"
=ROMAN(1999,4) // returns "MIM"
Roman numbers
The table below lists available Roman numbers with their equivalent Arabic number value.
| Symbol | Value |
|---|---|
| I | 1 |
| V | 5 |
| X | 10 |
| L | 50 |
| C | 100 |
| D | 500 |
| M | 1000 |
The ROMAN function converts Arabic numbers to Roman numbers. Use the ARABIC function to convert Roman numbers to Arabic numbers.
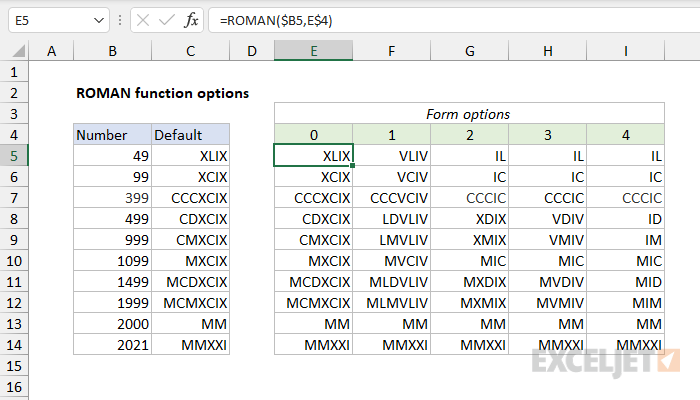
Abbreviated syntax
The ROMAN function can output Roman numbers in a more abbreviated syntax, controlled with the form argument. The screen below shows how different values for form affect output.
Notes
- Number should be a positive number between 1 and 3999.
- Number should be a whole number; decimal values are ignored.
- If number is negative or out of range, ROMAN returns #VALUE!
- The ROMAN function performs the opposite conversion as the ARABIC function.
- The form argument controls Roman numeral abbreviation. Valid inputs are 0-4.









