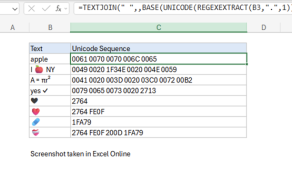
Purpose
Return value
Syntax
=BASE(number,radix,[min_length])- number - The number to convert to a given base.
- radix - The base to convert to.
- min_length - [optional] The minimum string length to return, achieved by padding with zeros.
Using the BASE function
The BASE function converts a number to a given base and returns the result as a text string. Base is specified with the radix argument.
The BASE function takes three arguments: number, radix, and min_length. Number should be an integer between 1 and 2^53. If number is negative, BASE returns a #NUM! error. The radix argument is used to specify base. Radix represents the number of digits used to represent numbers and should be an integer between 2 and 36. The optional min_length argument is the minimum string length that BASE should return. When min_length is provided, BASE will pad the output with zeros as needed to achieve the length specified.
Examples
The radix argument specifies base and the output from the BASE function is a text string. For example, the formulas below convert the number 13 into text representations of 13 in base 2 (binary), base 10 (decimal), and base 16 (hexadecimal):
=BASE(13,2) // returns "1101"
=BASE(13,10) // returns "13"
=BASE(13,16) // returns "D"
In the worksheet shown, the input numbers are being converted to three different representations: base 2 (binary), base 10 (decimal), and base 16 (hexadecimal). The formulas in D5, E5, and F5 are:
=BASE(B5,2) // base 2
=BASE(B5,10) // base 10
=BASE(B5,16) // base 16
The function also offers an optional argument min_length which will pad the returned string with zeros when its length is less than the given value. For example, the formulas below require a minimum length of 4:
=BASE(3,2,4) // returns "0011" as text
=BASE(10,16,4) // returns "000A" as text
DECIMAL function
The DECIMAL function performs the opposite conversion as the BASE function:
=BASE(100,2) // returns "1100100"
=DECIMAL("1100100",2) // returns 100
See more on the DECIMAL function here.
Notes
- The result from BASE is a text string.
- If number is negative, BASE returns a #NUM! error.
- BASE expects integers; decimal values are ignored.